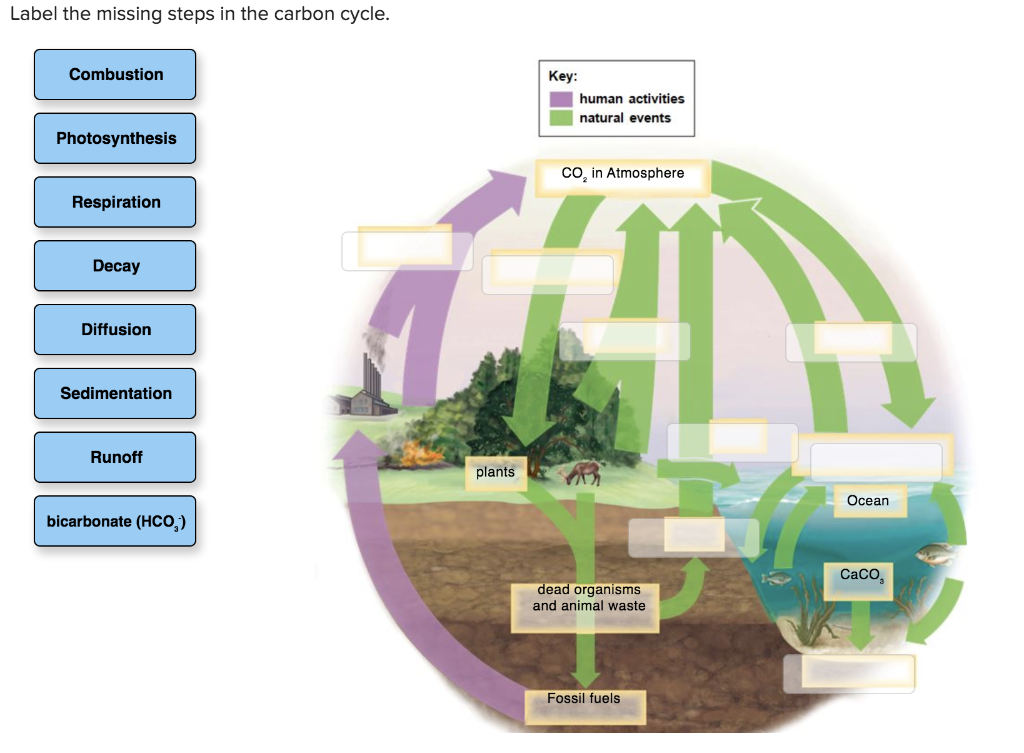
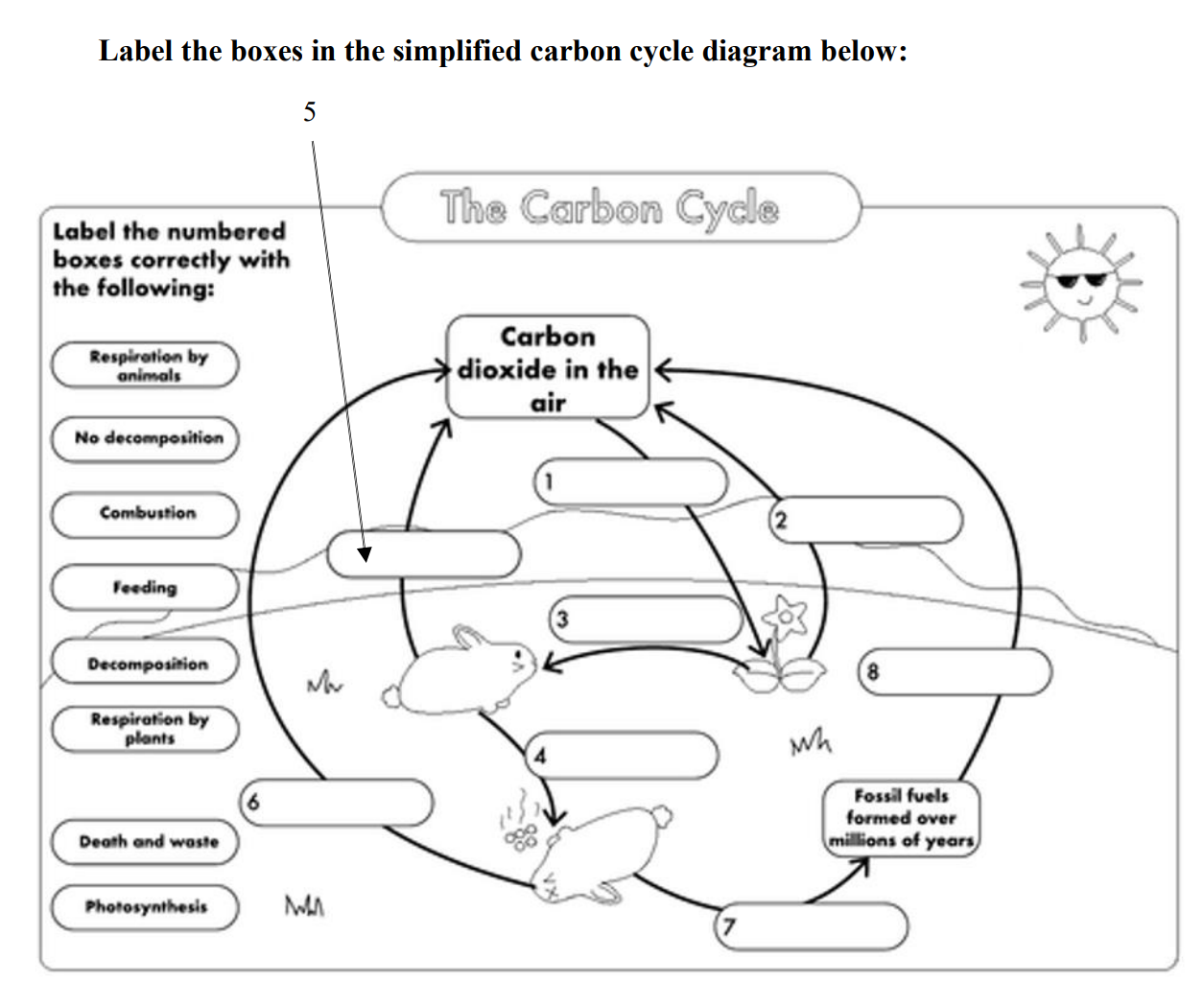
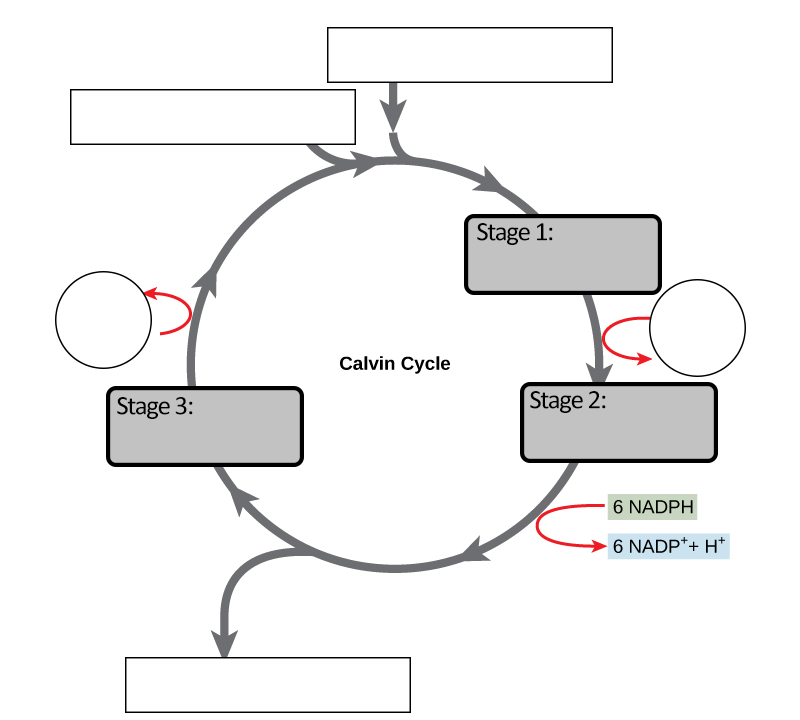
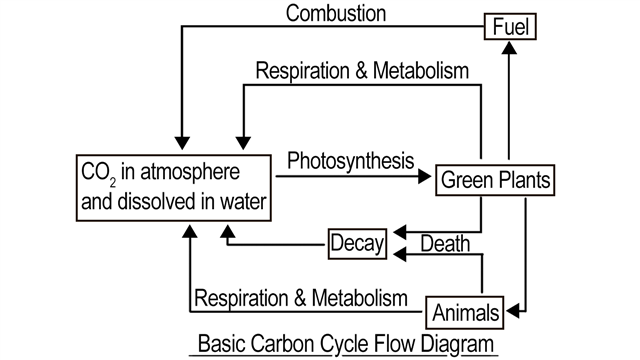
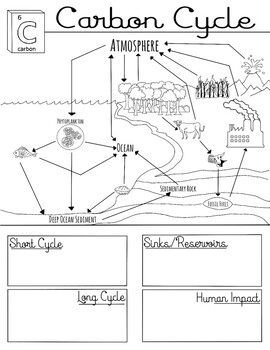
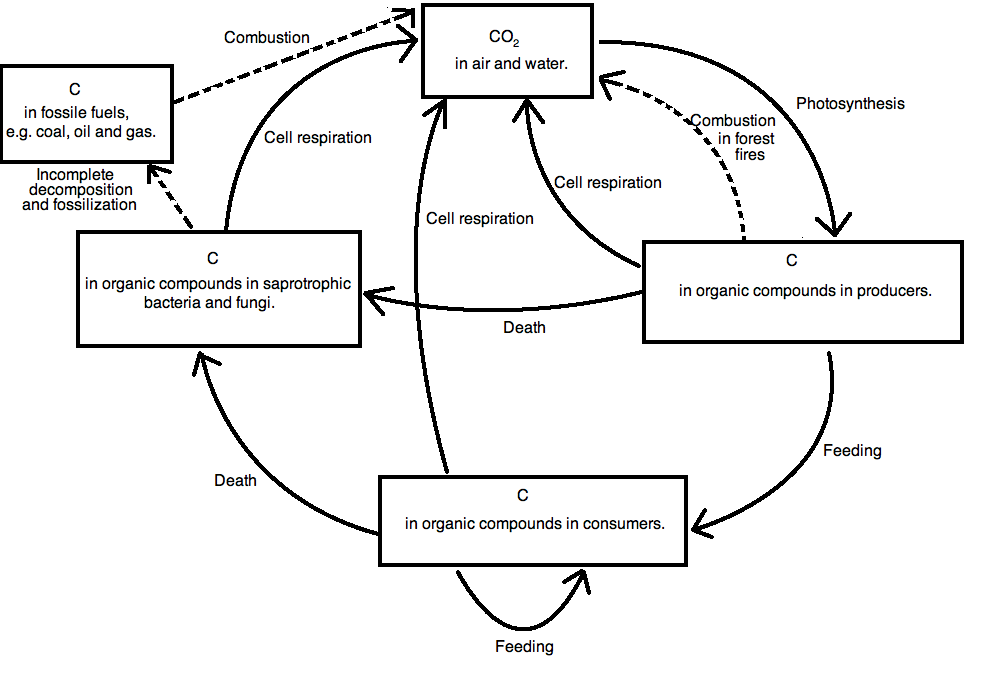
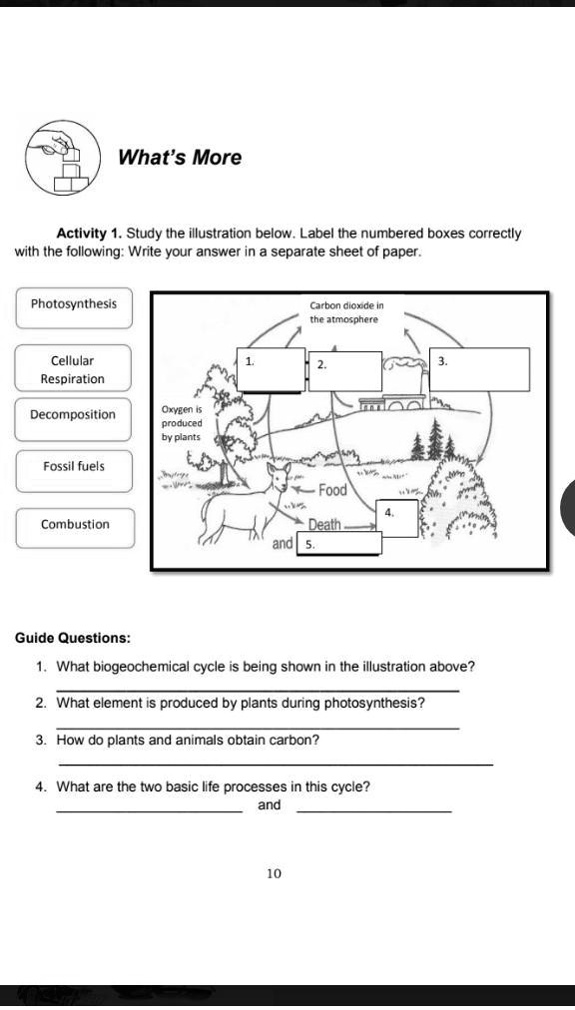
41 carbon cycle to label
Carbon Cycle Diagram | Center for Science Education Carbon Cycle Diagram UCAR This fairly basic carbon cycle diagram shows how carbon atoms 'flow' between various 'reservoirs' in the Earth system. This depiction of the carbon cycle focusses on the terrestrial (land-based) part of the cycle; there are also exchanges with the ocean which are only hinted at here. Revisiting the promise of carbon labelling | Nature Climate Change Shewmake et al. 51 suggested four criteria for selecting the most promising products for carbon labelling: (1) the amount of GHG emissions; (2) the availability of data on life-cycle emissions;...
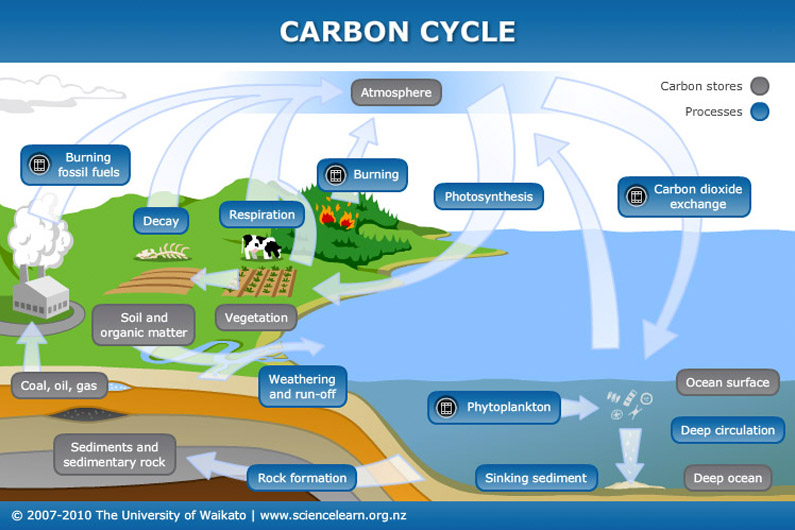
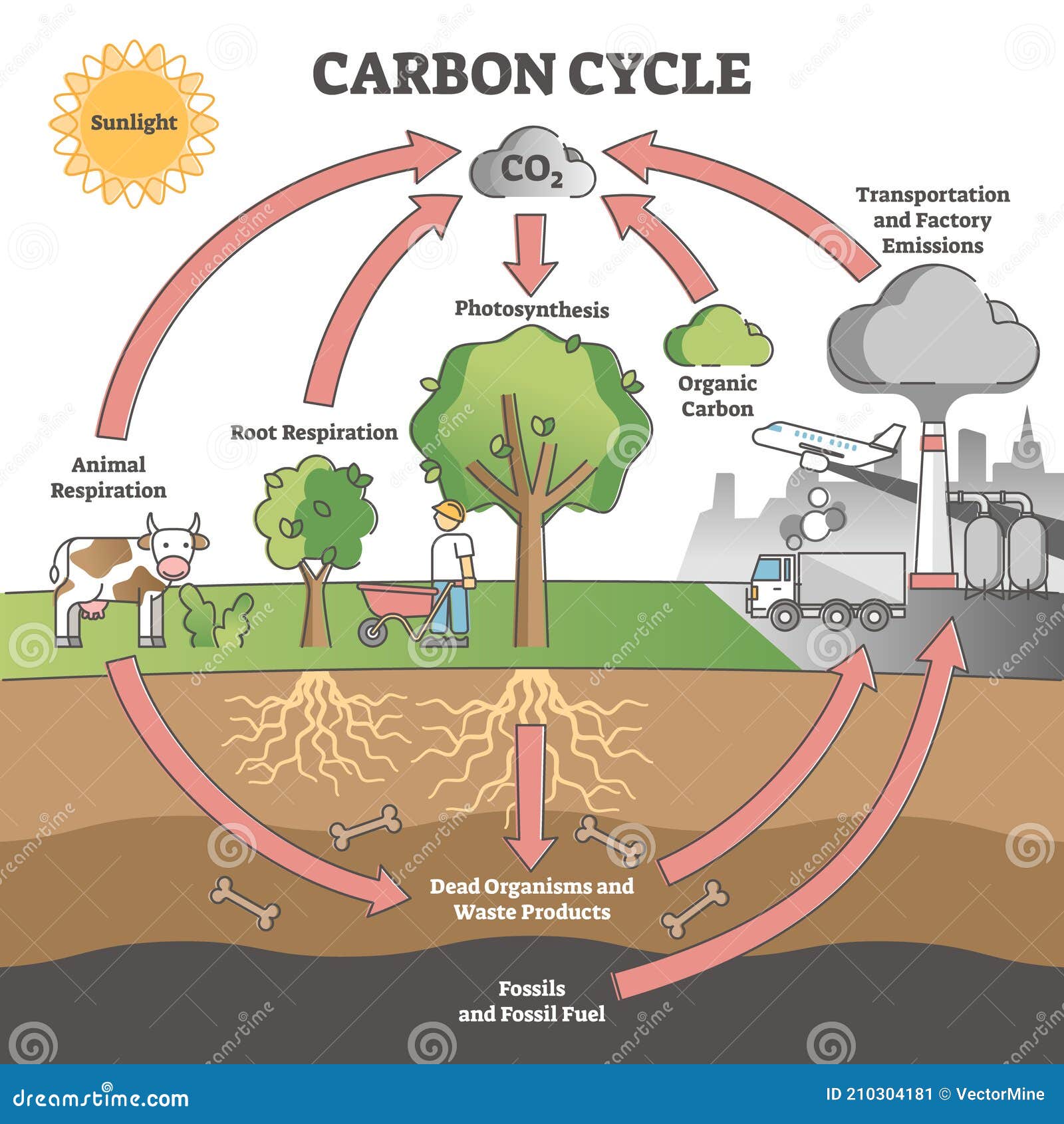
Carbon cycle | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Carbon compounds regulate the Earth's temperature, make up the food that sustains us, and provide energy that fuels our global economy. The carbon cycle. (NOAA) Download Image Most of Earth's carbon is stored in rocks and sediments. The rest is located in the ocean, atmosphere, and in living organisms.

Carbon cycle to label
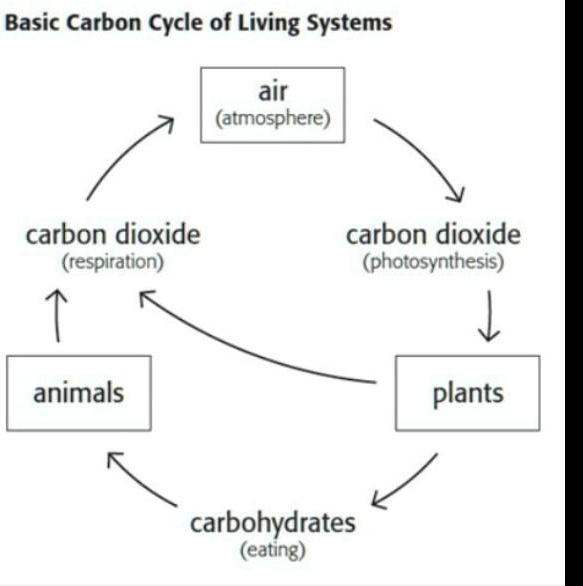
What is the carbon cycle? - National Ocean Service The carbon cycle describes the process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere to the Earth and then back into the atmosphere. Since our planet and its atmosphere form a closed environment, the amount of carbon in this system does not change. Where the carbon is located — in the atmosphere or on Earth — is constantly in flux. Carbon Cycle and Ecosystems | Terra Carbon is a fundamental part of the Earth system. It is one of the primary building blocks of all organic matter on Earth and a key element in setting Earth's temperature. Carbon moves from the atmosphere to the land, ocean, and life through biological, chemical, geological and physical processes in a cycle called the carbon cycle. Carbon Cycle: Importance, Process & Diagram - Collegedunia The photosynthesis process involves the absorption of CO 2 by plants to produce carbohydrates. The equation is as follows: CO2 + H2O + energy → CH2O + O2. Carbon Cycle on Land. Carbon compounds pass through the food chain from producer to consumer. Most of the carbon is found in the body in the form of carbon dioxide through respiration.
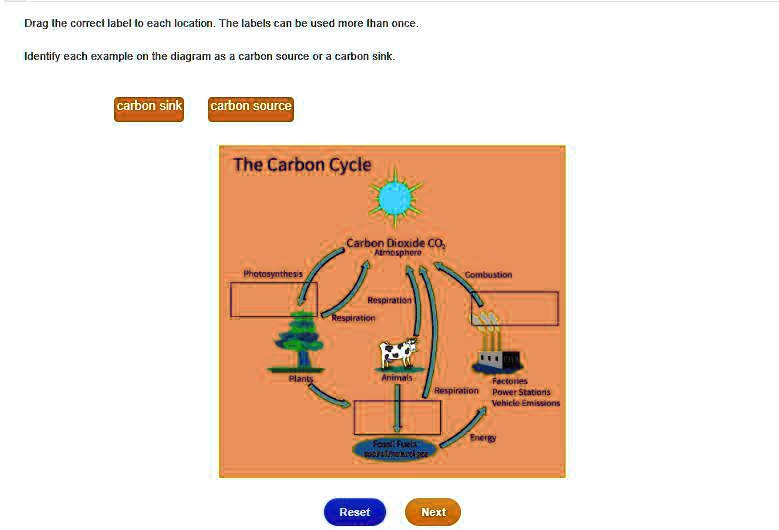
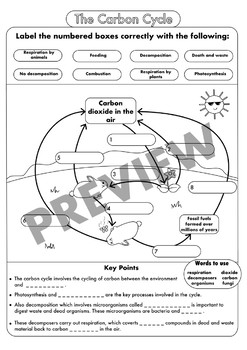
Carbon cycle to label. GCSE Carbon Cycle A4 poster to label (sample worksheet) GCSE Carbon Cycle A4 poster to label (sample worksheet) Subject: Biology Age range: 14-16 Resource type: Worksheet/Activity 28 reviews File previews pdf, 126.27 KB pdf, 175.99 KB An A4 poster of the Carbon Cycle for GCSE Biology students to label and learn the key parts of the carbon cycle. The Carbon Cycle - NASA Carbon flows between each reservoir in an exchange called the carbon cycle, which has slow and fast components. Any change in the cycle that shifts carbon out of one reservoir puts more carbon in the other reservoirs. Changes that put carbon gases into the atmosphere result in warmer temperatures on Earth. Carbon cycle - Wikipedia The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major component of many minerals such as limestone. The Carbon Cycle interactive | NOAA Climate.gov The Carbon Cycle interactive, The Carbon Cycle interactive, The Carbon Cycle interactive This is an interactive visualization of the Carbon Cycle, through short-term and long-term processes. Click to View Notes from our reviewers The CLEAN collection is hand-picked and rigorously reviewed for scientific accuracy and classroom effectiveness.
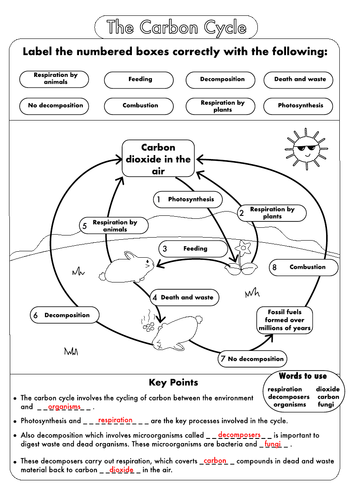
Carbon Cycle - Definition, Process, Diagram Of Carbon Cycle - BYJUS Carbon Cycle is a biogeochemical cycle where various carbon compounds are interchanged among the various layers of the earth, namely, the biosphere, geosphere, pedosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere. What are the 4 steps of the carbon cycle? Carbon enters the atmosphere as CO2 CO2 is absorbed by autotrophs such as green plants The carbon cycle (article) | Ecology | Khan Academy The biological carbon cycle Carbon enters all food webs, both terrestrial and aquatic, through autotrophs, or self-feeders. Almost all of these autotrophs are photosynthesizers, such as plants or algae. Autotrophs capture carbon dioxide from the air or bicarbonate ions from the water and use them to make organic compounds such as glucose. Coloring Page: The Carbon Dioxide Cycle The carbon dioxide cycle is the movement of carbon dioxide (CO 2) between the land, the atmosphere, and the ocean. Print this page to color with your kids at home. (The downloadable PDF comes with a second page of definitions for each labeled term.) The activity is also available in Spanish on this page and here. Credit NASA/JPL-Caltech Enlarge INSIGHT: Carbon footprint labelling - a growing trend among ... - ICIS Some companies such as the dairy-free milk firm, Oatly Inc. or Quorn, the meat substitute brand, already have introduced carbon dioxide emissions information on their product labels. A product carbon footprint is the full inventory of all greenhouse gas emissions released throughout the product life-cycle. It is important to define the scope ...
The Carbon Cycle | National Geographic Society carbon cycle noun series of processes in which carbon (C) atoms circulate through Earth's land, ocean, atmosphere, and interior. fossil noun remnant, impression, or trace of an ancient organism. marine adjective having to do with the ocean. ocean noun large body of salt water that covers most of the Earth. organism noun living or once-living thing. Modeling the Carbon Cycle to Inform Others - National Geographic Society Noun. gas in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and ozone, that absorbs solar heat reflected by the surface of the Earth, warming the atmosphere. hydrologic cycle. Noun. system of recycling liquid, gas, and solid water throughout a planet. Also called the water cycle. photosynthesis. Carbon cycle — Science Learning Hub In fossil fuels, the carbon is stored in long-chain hydrocarbons, and then through combustion with oxygen in our cars or in factories, the carbon is converted to CO 2, which is released to the atmosphere. And in addition, a number of other byproducts are also produced through inefficiencies in combustion like CO which are atmospheric pollutants. What does carbon impact look like on a food label? The carbon label, however, is fairly new. A carbon label denotes how much carbon dioxide is released to the atmosphere throughout a product's life cycle, as a proxy for climate impact. It could someday function similar to a Nutrition Facts label, informing customers on environmental impact instead of nutritional content. Companies using the ...
Title: The Carbon Cycle Name - Utah Education Network 1. Read the selection below about the carbon cycle. 2. As you read, draw what happens to carbon as it travels through the cycle. 3. Use arrows to show when carbon moves from one place to the next. 4. Make sure to label your drawing and include captions that explain where the carbon is, and what is happening to it as it moves from place to place.
Make a Carbon Cycle Diagram - Storyboard That Click "Start Assignment". Find an appropriate scene to show the carbon cycle. Add characters and items as necessary. Use arrows to show the movement of carbon in the carbon cycle among the atmosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere and geosphere. Label the main parts of the carbon cycle with Textables and arrows. Add extra information about the carbon ...
Carbon Cycle: Importance, Process & Diagram - Collegedunia The photosynthesis process involves the absorption of CO 2 by plants to produce carbohydrates. The equation is as follows: CO2 + H2O + energy → CH2O + O2. Carbon Cycle on Land. Carbon compounds pass through the food chain from producer to consumer. Most of the carbon is found in the body in the form of carbon dioxide through respiration.
Carbon Cycle and Ecosystems | Terra Carbon is a fundamental part of the Earth system. It is one of the primary building blocks of all organic matter on Earth and a key element in setting Earth's temperature. Carbon moves from the atmosphere to the land, ocean, and life through biological, chemical, geological and physical processes in a cycle called the carbon cycle.
What is the carbon cycle? - National Ocean Service The carbon cycle describes the process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere to the Earth and then back into the atmosphere. Since our planet and its atmosphere form a closed environment, the amount of carbon in this system does not change. Where the carbon is located — in the atmosphere or on Earth — is constantly in flux.

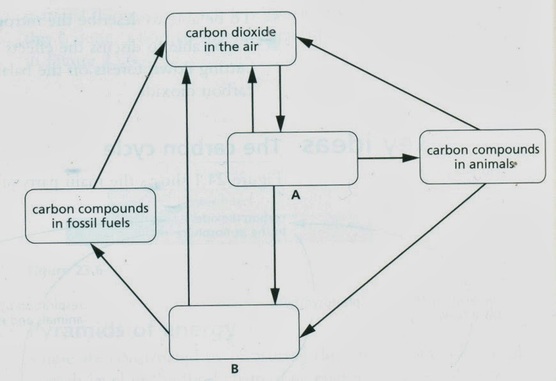
![Explain carbon cycle with the help of a diagram. [5 MARKS]](https://meritnation-question-images.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/byjus/infinitestudent-images/ckeditor_assets/pictures/13513/content_carbon_cycle.png)



















Komentar
Posting Komentar